1.
PACS
– Picture Archiving and Communication System
PACS is a medical imaging technology used to securely store and digitally transmit electronic images and clinical reports. Instead of manually carrying of file and store, retrieve and send sensitive information, films and reports, medical documentation and images are securely housed together and safely accessed essentially from anywhere in the world using PACS software, workstations and mobile devices.
2. DICOM – Digital images and communications in Medicine
DICOM is the international standard to communicate and manage medical images and data. It ensures the interoperability of systems used to produce, store, share, display, send, query, process, retrieve and print medical images, as well as to manage related workflows.
3. VNA – Vendor Neutral Archiving
A vendor neutral archive (VNA) is a technology that stores medical images in a standard format and interface, making them accessible to healthcare professionals regardless of what proprietary system created the images.
4. RIS – Radiology Information System
Radiology Information System is a networked software system for managing medical imagery and associated data. A RIS is especially useful for tracking radiology imaging orders and billing information, and is often used in conjunction with PACS and VNAs to manage image archives, record-keeping and billing.
5.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy is a type of medical imaging that shows a continuous X-ray image on a monitor. It is like an X-ray movie. During a fluoroscopy procedure, an X-ray beam is passed through the body. Fluoroscopy procedures are performed to help diagnose disease, or to guide physicians during certain treatment procedures.
6. CT Scan- Computerized Tomography Scan
CT scan is a form of computer-assisted imaging
that is assembled from many x-rays.
CT scan allows doctors and researchers to get detailed, highly accurate, 3D imaging of a body with depth into solid mass. This allows the inside of patients to be visually diagnosed without physical entry into the body. CT scans are used in diagnosing and analysis of: internal injuries, cancer, other tumors, blood clots or excess fluid and issues in the heart, liver, lungs, bones and joints.
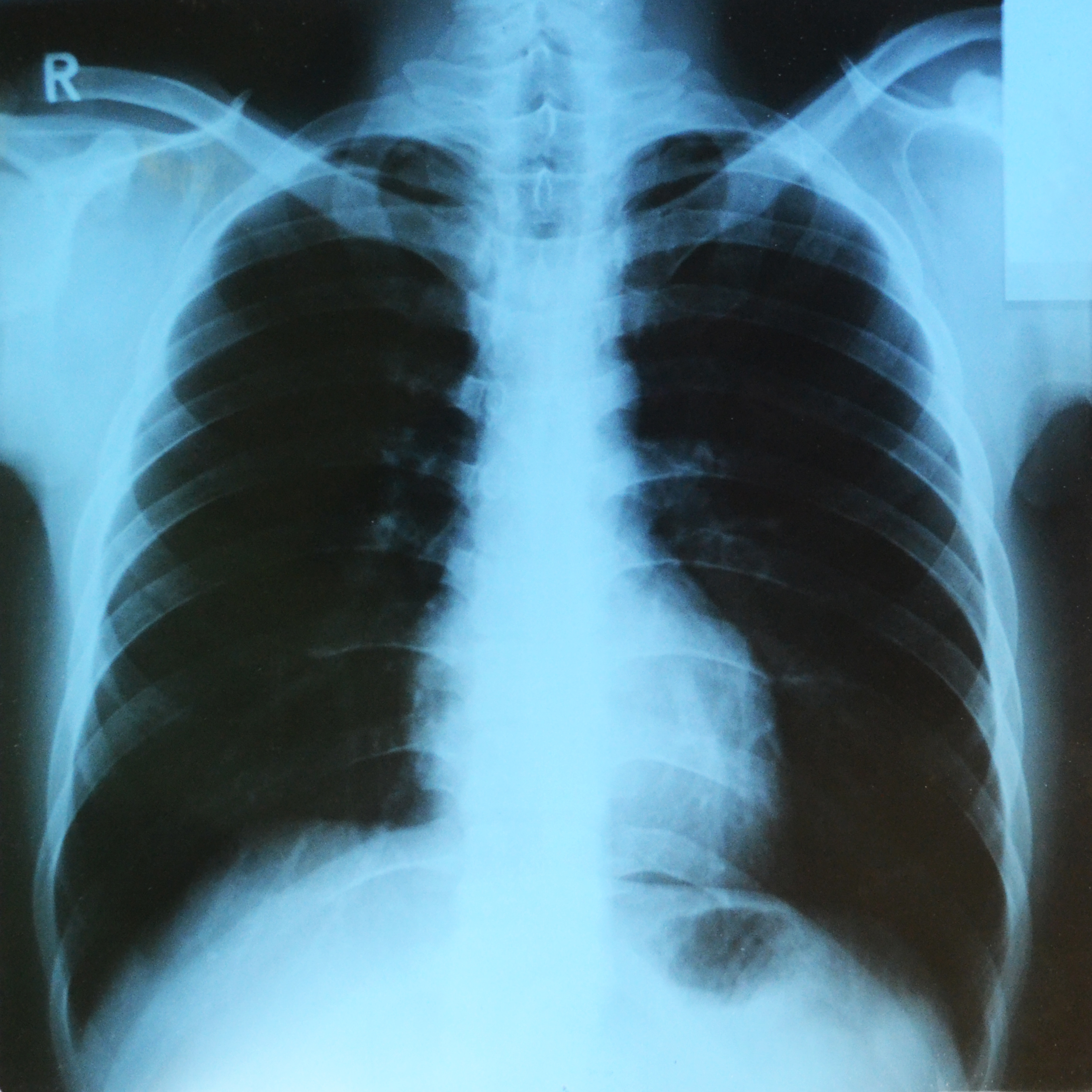
7. X-RAY Scan
X-ray scan or
radiography, is a diagnostic imaging technique that produces images of bones,
providing clear detail of the bony structure. The image below is Lungs-X-ray.
8. MRI Scan
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a method of obtaining
images of the interiors of objects, especially living things such as humans and
animals.
9. ECHO SCAN- Echocardiogram
Echo scan is used to look at the heart and nearby blood
vessels. Echo scan is a type of ultrasound scan, which implies that a small probe is used to send out
high-frequency sound waves that create echoes when they bounce off different
parts of the body.
10 ECG- Electrocardiogram
ECG is a test which measures the electrical activity of your heart to show whether or not it is working normally. An ECG records the heart’s rhythm and activity on a moving strip of paper or a line on a screen. Your doctor can read and interpret the peaks and dips on paper or screen to see if there is any abnormal or unusual activity.
When next you visit the hospital or a healthcare diagnostics center and hear any of these terms, you know the meaning.
Please subscribe and follow us.